As a common tool for processing internal threads, taps can be divided into spiral flute taps, spiral point taps, straight flute taps and pipe thread taps according to their shapes. According to the use environment, they can be divided into hand taps and machine taps. According to the sizes, divided into metric, American, and Inch taps. Are you familiar with them all?
Tap Classification
- Cutting tap
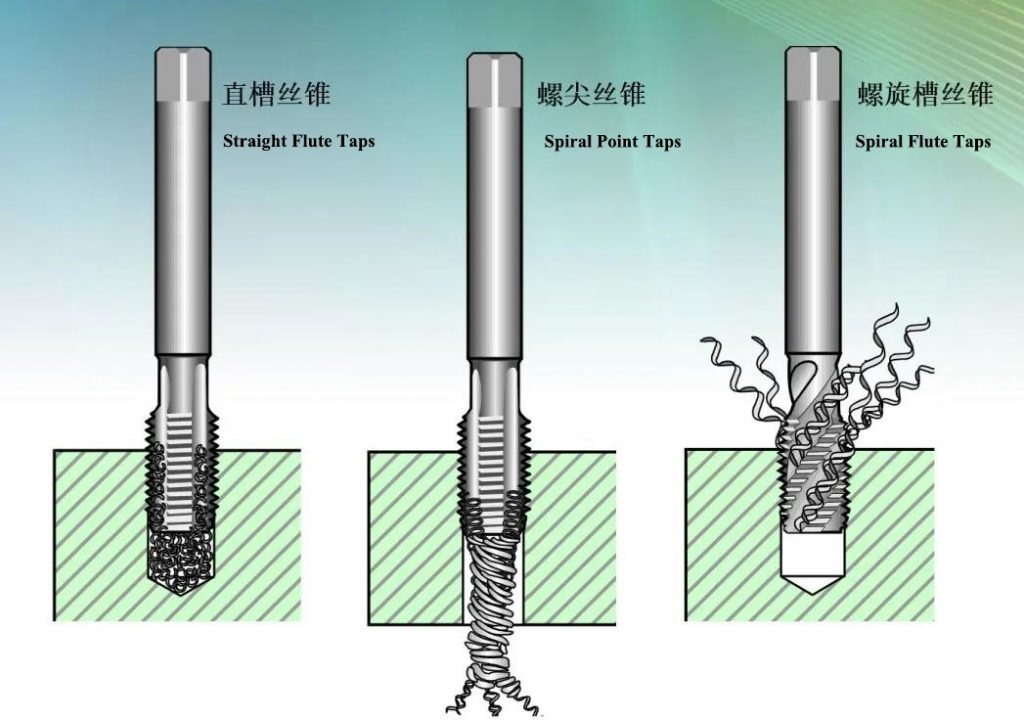
- Straight flute taps: used for the processing of through holes and blind holes. Iron filings are present in the tap grooves, and the thread quality of the processed threads is not high. It is more commonly used for the processing of the materials with short chip, such as gray cast iron.
- Spiral flute tap: used for blind hole machining with a hole depth less than or equal to 3D, iron filings are discharged along the spiral flute, and the thread surface quality is high.
10~20° helix angle tap can process thread depth less than or equal to 2D;
28~40° helix angle tap can process thread depth less than or equal to 3D;
The 50° helix angle tap can process the thread depth less than or equal to 3.5D (4D under special conditions).
In some cases (hard materials, large pitch, etc.), in order to obtain better tooth tip strength, spiral fluted taps are used to process through holes.
- Spiral point taps: usually only used for through holes, the ratio of length to diameter can reach 3D~3.5D, iron filings are discharged downwards, the cutting torque is small, and the surface quality of the processed thread is high. It is also called the blade inclination tap or Tip tap.
When cutting, it is necessary to ensure that all cutting parts are penetrated, otherwise tooth chipping will occur.
- Extrusion tap
It can be used for the processing of through holes and blind holes, forming a tooth profile through plastic deformation of the material, and can only be used for processing plastic materials.
Its main features:
1) Use the plastic deformation of the workpiece to process the thread;
2) The tap has a large cross-sectional area, high strength, and is not easy to break;
3) The cutting speed is higher than that of cutting taps, and the productivity is also improved accordingly;
4) Because it is cold extrusion processing, the mechanical properties of the thread surface after processing are improved, the surface roughness is high, and the thread strength, wear resistance and corrosion resistance are improved;
5) No chip processing.
The disadvantages are:
1) It can only be used for processing plastic materials;
2) High manufacturing cost.
There are two structural forms:
1) Extrusion taps without oil grooves are only used for blind hole vertical machining conditions;
2) Extrusion taps with oil grooves are suitable for all working conditions, but usually small diameter taps are not designed with oil grooves due to the difficulty of manufacturing.
Structural parameters of the tap
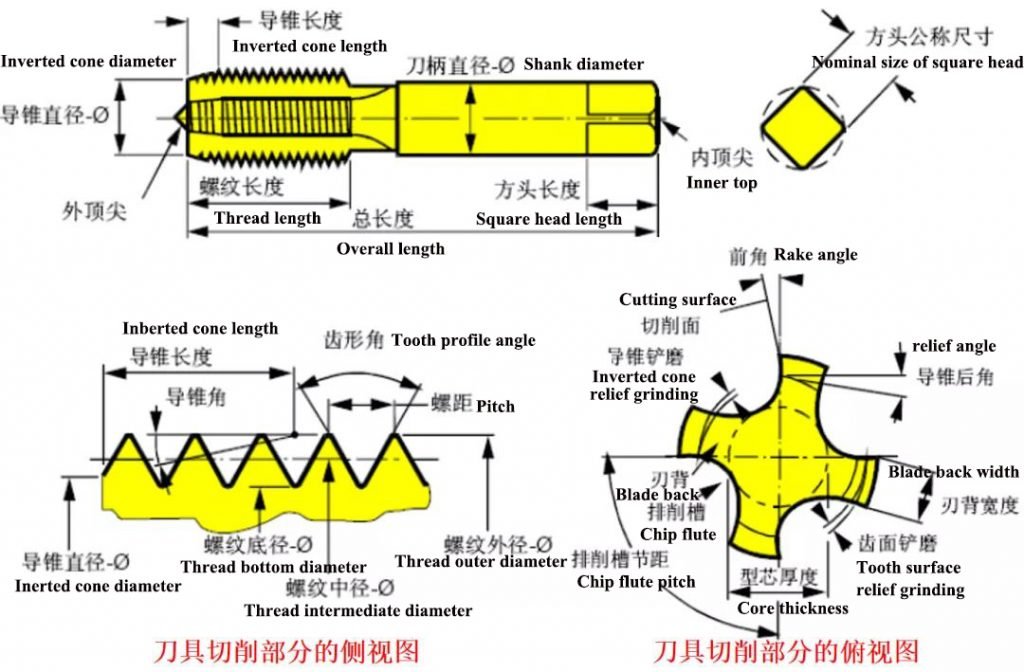
(1) Dimensions
1) Total length: some working conditions that require special extra length need to be paid attention to
2) Slot length: Same as above
3) Shank side: At present, the common shank side standards include DIN (371/374/376), ANSI, JIS, ISO, etc. Please pay attention to the matching relationship with the tapping tool holder when selecting
(2) Threaded part
1) Accuracy: It is selected by the specific thread standard. The metric thread ISO1/2/3 is equivalent to the national standard H1/2/3, but the manufacturer’s internal control standards should be paid attention to.
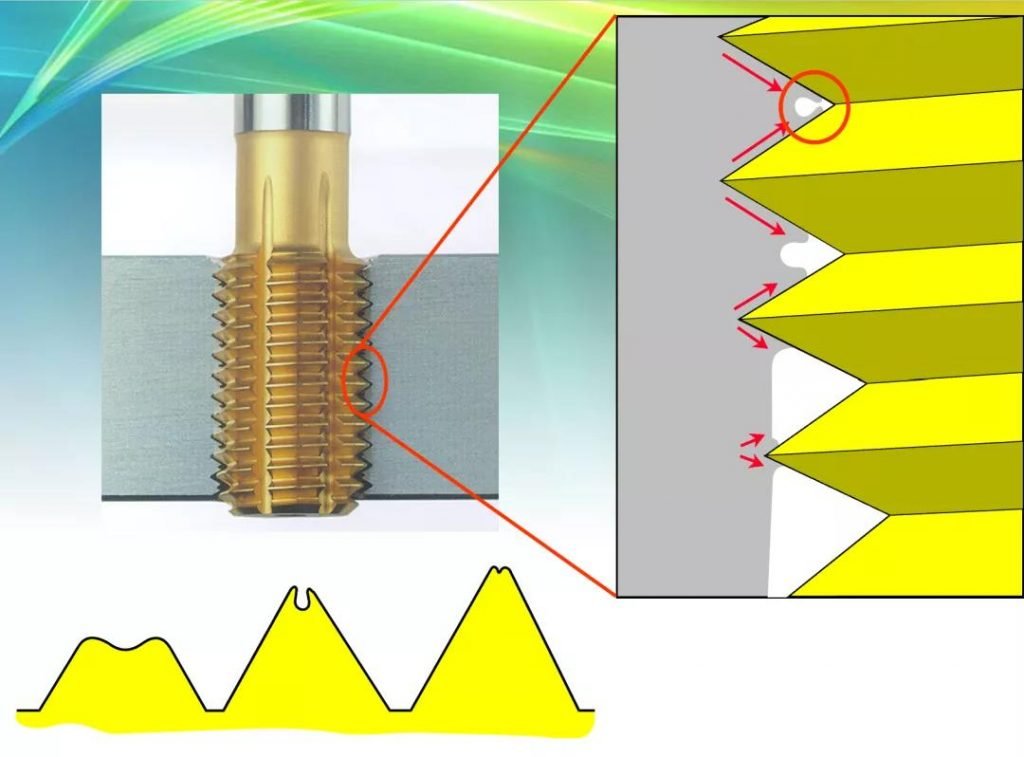
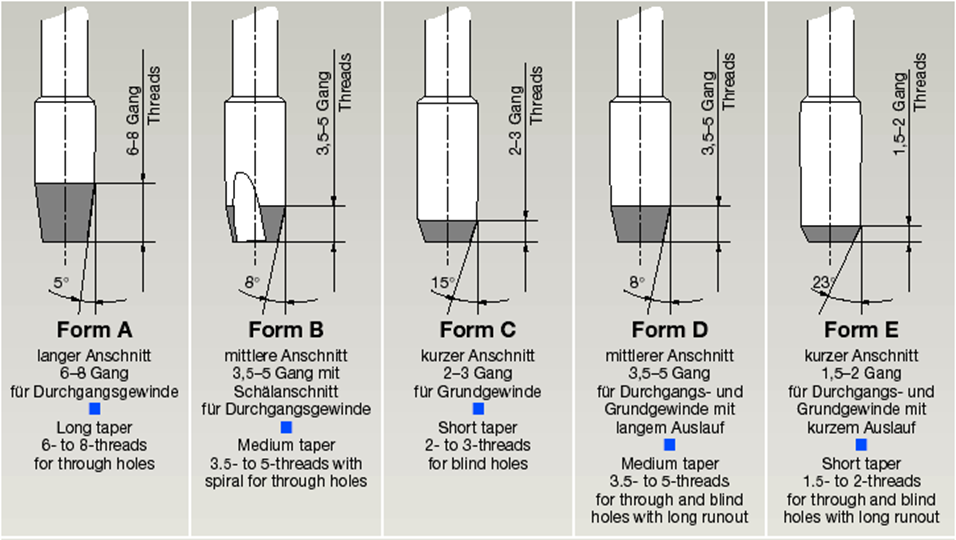
- Cutting cone: The cutting part of the tap has formed a partial fixed pattern. Generally, the longer the cutting cone, the better the life of the tap.
- Correction teeth: play an auxiliary and correction role, especially in the unstable working conditions of the tapping system, the more correction teeth, the greater the tapping resistance.
(3) Chip flute
1. Groove: It affects the forming and discharge of iron filings, which is usually the internal secret of each manufacturer.
2. Rake angle and relief angle: The tap becomes sharp when it increases, which can significantly reduce the cutting resistance, but the strength and stability of the tooth tip decrease, and the relief angle is the relief angle.
- Number of grooves: increasing the number of grooves and increasing the number of cutting edges can effectively increase the life of the tap; but it will compress the chip removal space, which is unfavorable for chip removal.
Material and coating of the tap
(1) The material of the tap
1) Tool steel: It is mostly used for hand incisor taps, which are not common anymore.
2) high-speed steel without Cobalt: At present, it is widely used as tap material, such as M2 (W6Mo5Cr4V2, 6542), M3, etc., and the mark code is HSS.
3) Cobalt-containing high-speed steel: At present, it is widely used as tap material, such as M35, M42, etc., and the marking code is HSS-E.
4) Powder metallurgy high-speed steel: used as a high-performance tap material, the performance is greatly improved compared with the above two, and the naming methods of each manufacturer are also different, and the marking code is HSS-E-PM.
5) Cemented carbide materials: usually select ultra-fine particles, good toughness grades, mainly used to manufacture straight-groove taps processing short chip materials, such as gray cast iron, high silicon aluminum, etc.
The tap is highly dependent on the material, and the selection of good materials can further optimize the structural parameters of the tap, making it suitable for efficient and more demanding working conditions, and at the same time have a higher life. At present, major tap manufacturers have their own material factories or material formulas. At the same time, due to cobalt resources and price issues, new high-performance high-speed steels without cobalt have also come out.
- Coating of tap
1) Steam oxidation: the tap is placed in high-temperature water vapor to form an oxide film on the surface, which has good adsorption to the coolant, which can reduce friction and prevent adhesion between the tap and the material to be cut. Suitable for processing mild steel.
2) Nitriding treatment: the surface of the tap is nitrided to form a surface hardened layer, which is suitable for processing cast iron, cast aluminum and other materials that have a lot of tool wear.
3) Steam + Nitriding: Combining the advantages of the above two.
4) TiN: Golden yellow coating, with good coating hardness and lubricity, and good coating adhesion, suitable for processing most materials.
5) TiCN: Blue-gray coating, hardness is about 3000HV, heat resistance up to 400°C.
6) TiN+TiCN: dark yellow coating, with excellent coating hardness and lubricity, suitable for processing most materials.
7) TiAlN: Blue-gray coating, hardness 3300HV, heat resistance up to 900°C, can be used for high-speed processing.
8) CrN: Silver-gray coating, excellent lubrication performance, mainly used for processing non-ferrous metals.
The coating of the tap has a very obvious effect on the performance of the tap, but at present, most manufacturers and coating manufacturers cooperate to study special coatings separately.
